
Bed Bugs in Virginia
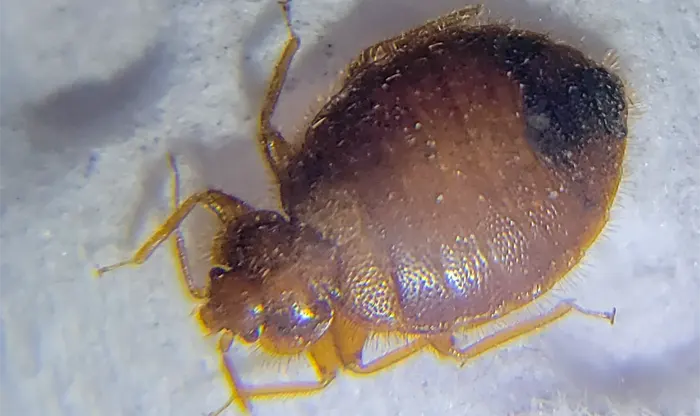
Proper identification of bed bugs is crucial for effective control and prevention of infestations. It is important to note that bed bugs are tiny, flat, and oval-shaped insects, with a reddish-brown coloration. They are wingless but are incredibly adept climbers, allowing them to easily crawl up walls, furniture, and even ceilings. Adult bed bugs are typically about 4 to 5 mm long, roughly the size of an apple seed. They have six legs and two antennae, which they use to sense their surroundings and locate their prey.
It is easy to mistake bed bugs for other insects, such as carpet beetles, cockroaches, or ticks. However, bed bugs have several unique features that set them apart from other pests. They have a distinct body shape, with a flattened appearance that allows them to easily hide in cracks and crevices. Additionally, they have a beak-like mouthpart that they use to pierce the skin of their hosts and feed on their blood. By learning how to properly identify bed bugs, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent and control infestations in their homes and communities.
Bed Bug Life Cycle
Understanding the life cycle and behavior of bed bugs is crucial for effective control and prevention. Bed bugs go through a gradual metamorphosis, which means they develop in stages from egg to nymph to adult. The following is a brief overview of the bed bug life cycle
- 1
Egg: A female bed bug can lay up to five eggs per day, which are usually deposited in cracks and crevices near a food source. Bed bug eggs are approximately 1mm in size and are usually laid in clusters.
- 2
Nymph: Bed bug eggs hatch into nymphs, which resemble smaller versions of adult bed bugs. Nymphs require a blood meal to molt into the next stage of development, and they will molt five times before becoming an adult.
- 3Adult: Once bed bugs reach adulthood, they can reproduce and continue to feed on human blood. Adult bed bugs can survive for up to six months without a blood meal, which allows them to persist even when food sources are scarce.

Egg

Nymph

Adult

Bed Bug Behavior
Bed bugs are primarily nocturnal and are attracted to body heat and carbon dioxide, which are both emitted by humans. They typically feed on exposed skin, such as the face, neck, arms, and legs, and will often feed in a linear pattern. Bed bugs can go unnoticed for long periods, as their bites do not always cause immediate symptoms. In addition to feeding on humans, bed bugs can also feed on pets and other warm-blooded animals.
Bed bugs prefer to live in cracks and crevices near their food source, which includes beds, furniture, and other areas where people sleep or rest. However, they can also be found in other areas, such as baseboards, electrical outlets, and behind wallpaper. Bed bugs can be introduced into a home or building through infested furniture or clothing, or they can travel between adjoining rooms or apartments through wall voids or electrical conduits.
Effective control and prevention of bed bugs require a comprehensive approach that targets all life stages and focuses on reducing or eliminating their access to human hosts.
Bed bugs are a common pest problem in Virginia, and their distribution is not limited to any specific region or area. They are found in both urban and rural areas and can infest any type of building, including single-family homes, apartments, hotels, and commercial buildings.
- 1
Bites: Bed bug bites are usually the first sign of an infestation. They are often clustered in groups or lines and can cause itchiness and swelling. Bed bug bites are not always immediately noticeable and can take several days to appear.
- 2Blood stains: Bed bugs leave behind blood stains on sheets and pillowcases from their bites. The stains are typically dark red or brown and may be visible on the bedding or mattress.
- 3Fecal spots: Bed bugs leave behind dark, rust-colored fecal spots on mattresses, bedding, and other surfaces where they rest or feed. These spots may be visible to the naked eye and can be an indication of a large infestation.
- 4Shed skins: Bed bugs shed their skins as they grow and develop. These skins are usually found near areas where bed bugs hide, such as along mattress seams, headboards, and baseboards.
- 5Live bed bugs: Although bed bugs are excellent at hiding, they can sometimes be seen crawling on mattresses, bedding, or furniture. Adult bed bugs are approximately the size and shape of an apple seed, and nymphs are smaller and lighter in color.
Bed bugs are a common pest problem in Virginia and can be found in all types of buildings, including homes, apartments, and hotels. They are difficult to detect and can quickly infest a building if left untreated. Bed bugs are attracted to human body heat and carbon dioxide, which makes sleeping areas, couches, and chairs prime habitats for them.
Although bed bugs are not known to transmit diseases, their bites can cause discomfort and itchiness, and severe infestations can cause anxiety and sleeplessness. Effective control of bed bugs in Virginia requires a comprehensive approach, including thorough inspection, treatment of infested areas, and ongoing monitoring.
Prevention is key when it comes to bed bug control, and property owners and landlords have a legal responsibility to keep their buildings free of bed bugs. Tenants should notify their landlord or property owner immediately if they suspect a bed bug infestation.
In Virginia, the Department of Health regulates bed bugs as a public health nuisance, and property owners and landlords must comply with regulations to prevent and control infestations.
Do You Have a Bed Bug Problem?
Learn more about our Bed Bug Removal Program or call us at (540) 776-1769


